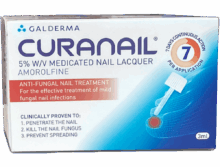
Fungal Nail Infection
A fungal nail infection, also known as onychomycosis, is a common condition that often starts off as a white or yellow spot beneath the tip of your toe or fingernail. As the infection progresses and spreads, the fungus can cause discolouration and thickness of the nail and. Severe cases can cause parts the nail to fall off or crumble at the edge. This can spread across several nails.